Central African Republic
- Australia
- Benin
- Brunei
- Burkina Faso
- Cameroon
- Canada
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Colombia
- Côte d’Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Denmark
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- France
- Germany
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Indonesia
- India
- Iran
- Iraq
- Ireland
- Jordan
- Kenya
- Kuwait
- Liberia
- Malawi
- Malaysia
- Mali
- Malta
- Mauritania
- Mexico
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Oman
- Pakistan
- Peru
- Portugal
- Russia
- Saudi Arabia
- Senegal
- Sierra Leone
- Singapore
- Somalia
- Somaliland
- South Sudan
- Spain
- Sudan
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Tanzania
- Thailand
- The Gambia
- The Maldives
- Togo
- Uganda
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States of America
- Yemen
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
Population
4.75 million
Estimated prevalence among girls and women aged 15-49
24%
2018 population growth rate
1.68%
Estimated prevalence among girls and women aged 15-19
17.9%
Type practised
The most widely practised forms of female genital cutting (FGC) in the Central African Republic are Type I and Type II.
Age
The majority of girls are cut between the ages of ten and 14.
Source: 28 Too Many
Agent
The vast majority of girls in the Central African Republic who have undergone FGC were cut by traditional practitioners (95%).
Source: UNICEF, MICS 2010
Legal status
Illegal. FGC has been illegal in the Central African Republic since 1966. Anti-FGC law was further strengthened in 1996 and 2006.
National progress
- 1966 – Order No. 66/16 made FGC in the Central African Republic illegal (penalties unclear)
- 2001 – National Committee to Curb Traditional Practices Harmful to the Health of Women and Girls and Violence Against Women established by inter-ministerial decree
- 2006 – Protection of Women Against Violence Act introduced, the main law against FGC in the Central African Republic
- 2010 – Penal Code also criminalised FGC
Enforcement
It is not clear if any enforcement has taken place or any cases have been brought forward under the laws criminalising FGC.
The Central African Republic has been extremely unstable since its independence from France in 1960 and is one of the least developed countries in the world. Combatting FGC therefore remains an ongoing challenge.
Human Development Index ranking
188 in 2018 index, based on 2017 data.
Infant mortality rate
92 deaths per 1,000 live births (2015).
Source: 28 Too Many
Maternal mortality rate
882 deaths per 100,000 live births (2015).
Source: 28 Too Many
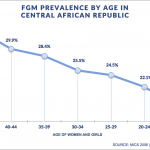
Trends in FGC prevalence
There is little evidence available regarding current efforts to abandon FGC in the Central African Republic. However, the prevalence among women aged 15-49 has declined over time (1994-2010) from 43% to 24%.
Prevalence breakdown
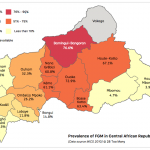
By region
FGC is widely practised across the Central African Republic, though prevalence rates vary. It is most prevalent in the country’s centre regions: Bamingui-Bangoran (76.6%), Ouaka (72.9%) and Haute-Kotto (67.1%). This contrasts with prevalence rates between 3% and 4% in areas of the west and south-east.
Source: UNICEF, MICS 2010